Top Level Name
⌊ Superfamily (core) Enolase
⌊ Subgroup methylaspartate ammonia-lyase
⌊ Family methylaspartate ammonia-lyase
| Total |
100%  |
<100%  |
|||
| Functional domains | 154 | 0 | 154 | ||
| UniProtKB | 764 | 0 | 764 | ||
| GI | 1527 | 0 | 1527 | ||
| Structures | 6 | ||||
| Reactions | 1 | ||||
| Functional domains of this family were last updated on Nov. 22, 2017 | |||||
| New functional domains were last added to this family on May 7, 2015 | |||||
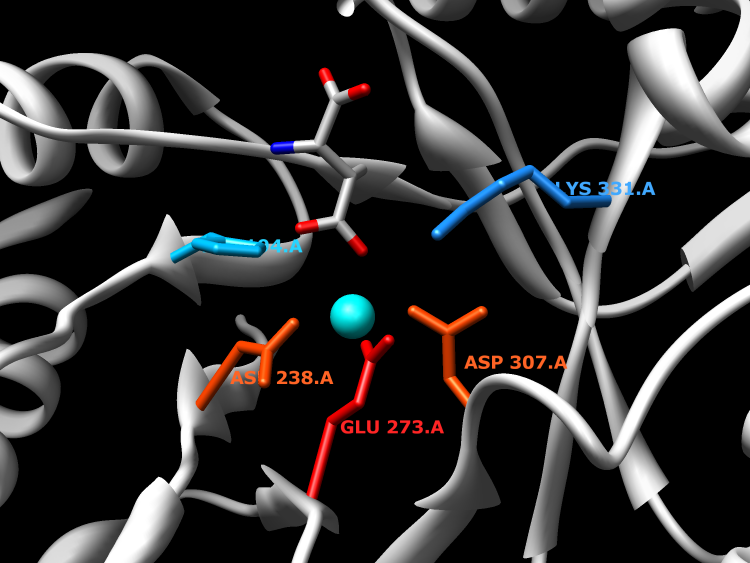
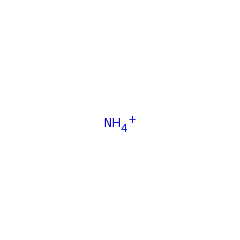
Enzymes in the beta-methylaspartate ammonia-lyase (MAL) family catalyze the reversible anti elimination of ammonia from L-threo-(2S,3S)-3-methylaspartic acid to form mesaconic acid, in the catabolic pathway for glutamate. Enzymes in the MAL family require an additional monovalent metal ion, beyond the one divalent metal required across all enzymes in the enolase superfamily, for optimal activity.
No References.
No notes.
Static File Downloads
| File Name | Description | Parameters | Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| network.fam7.bs60.mek250K.xgmml | One node per sequence network | min bit score = 60 max edge count = 250K |
size = 4.1M num_edges = 11781 num_nodes = 154 |
| sfld_alignment_fam7.msa | Annotated Sequence Alignment, Stockholm format | 7 sequences size: 4.4K |
Active Site