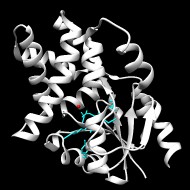
Top Level Name
⌊ Superfamily (core) Haloacid Dehalogenase
⌊ Subgroup C1.5: HAD, Beta-PGM, Phosphatase Like
⌊ C1.5.6: HAD, Beta-PGM, Phosphatase Like
⌊ Family 2-haloacid dehalogenase
| Total |
100%  |
<100%  |
|||
| Functional domains | 145 | 0 | 145 | ||
| UniProtKB | 549 | 0 | 549 | ||
| GI | 1125 | 0 | 1125 | ||
| Structures | 12 | ||||
| Reactions | 2 | ||||
| Functional domains of this family were last updated on Nov. 22, 2017 | |||||
| New functional domains were last added to this family on Aug. 1, 2014 | |||||
Enzymes in the 2-haloacid dehalogenase (HAD) family catalyze the hydrolytic dehalogenation of L-2-haloalkanoates to their corresponding d-2-hydroxyalkanoates with inversion of configuration at C2. Unlike most other members of the superfamily, HAD family members do not require a divalent metal ion cofactor.
Ridder, I.S., et al.
Crystal structures of intermediates in the dehalogenation of haloalkanoates by L-2-haloacid dehalogenase
▸ Abstract
J Biol Chem 1999;274(43):30672-30678 | PubMed ID: 10521454
No notes.
Static File Downloads
| File Name | Description | Parameters | Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| sfld_alignment_fam45.msa | Annotated Sequence Alignment, Stockholm format | 19 sequences size: 7.3K |
Active Site

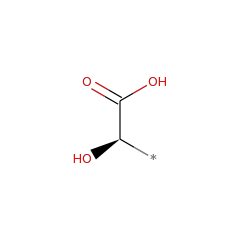
Catalyzed Reaction(s)
(S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-inverting)
 |
+ |  |
 |
 |
+ |  |
||
| (S)-2-haloacid 15791 |
water 15377 |
(2R)-2-hydroxy monocarboxylic acid 17893 |
halide anion 16042 |
EC: 3.8.1.2 | IntEnz: 3.8.1.2 | Kegg: 3.8.1.2 | BioCyc: 3.8.1.2 | BRENDA: 3.8.1.2
EC: | IntEnz: | Kegg: | BioCyc: | BRENDA: |