| Total |
100%  |
<100%  |
|||
| Functional domains | 13530 | 0 | 13530 | ||
| UniProtKB | 28511 | 0 | 28511 | ||
| GI | 53656 | 0 | 53656 | ||
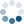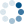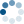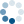
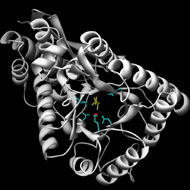
| Structures | 60 | ||||
| Reactions | 1 | ||||
| Functional domains of this family were last updated on Nov. 22, 2017 | |||||
| New functional domains were last added to this family on May 7, 2015 | |||||
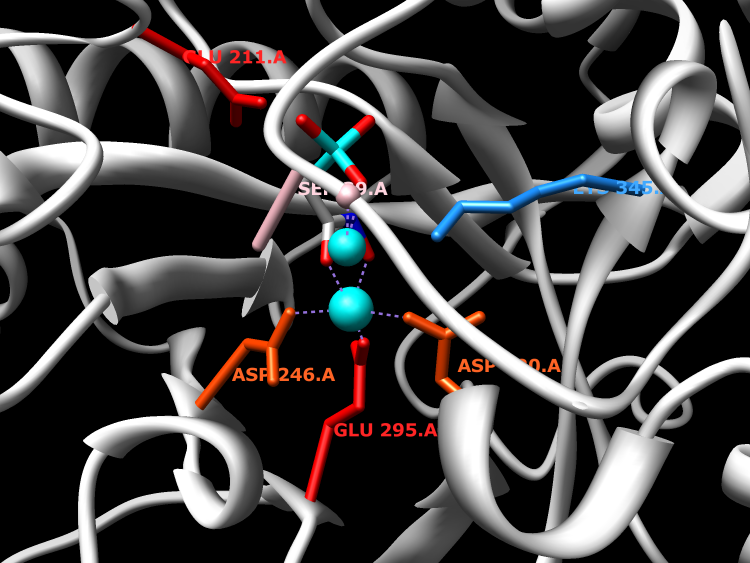
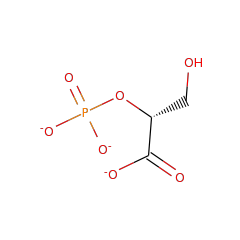
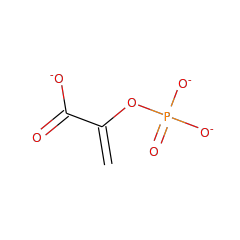
Enzymes in the enolase family catalyze the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate in the glycolytic pathway, and the reverse reaction in gluconeogenesis. Due to the ubiquitous nature of these pathways, the enolase family is quite large. Enzymes in the enolase family require an additional divalent metal ion, beyond the one divalent metal required across all enzymes in the superfamily, for optimal activity.
No References.
No notes.
Static File Downloads
| File Name | Description | Parameters | Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| repnet.fam2.th50.pE20.mek250K.xgmml | Representative network: each node is a group of similar sequences | node similarity threshold = 50 max edge count = 250K min -log10 E = 20 |
size = 7.4M num_edges = 5048 num_nodes = 101 |
| sfld_alignment_fam2.msa | Annotated Sequence Alignment, Stockholm format | 45 sequences size: 29K |
Total number of functional domains in this group.
Number of Functional Domains that have been manually or automatically been assigned to a family.
Number of Functional Domains that have not been assigned to a family.
Number of structures available from the PDB for members of this group.
Number of Functional Domains with 100% of Conserved Residues
Number of Functional Domains with less than 100% Conserved Residues
Active Site