Top Level Name
⌊ Superfamily (core) Radical SAM
⌊ Subgroup BATS domain containing
⌊ Family biotin synthase
| Total |
100%  |
<100%  |
|||
| Functional domains | 3245 | 3245 | 0 | ||
| UniProtKB | 9873 | 9873 | 0 | ||
| GI | 18996 | 18996 | 0 | ||
| Structures | 1 | ||||
| Reactions | 1 | ||||
| Functional domains of this family were last updated on June 10, 2017 | |||||
| New functional domains were last added to this family on Oct. 7, 2014 | |||||
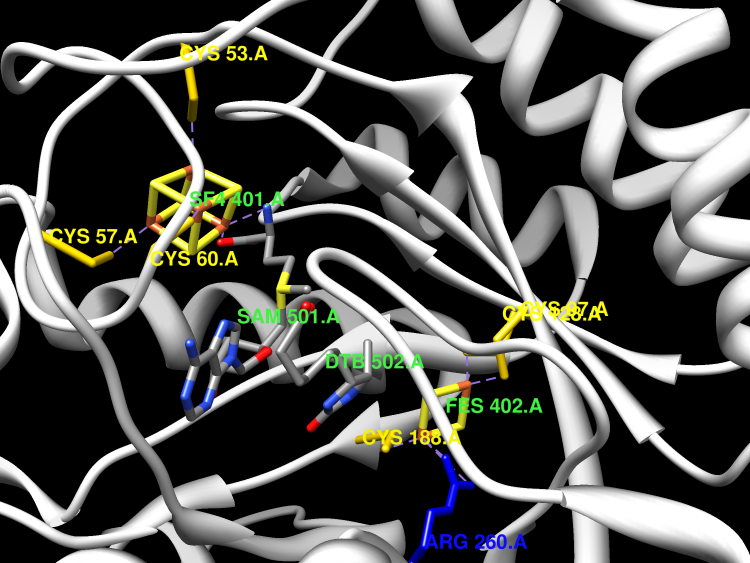
The enzyme binds a [4Fe-4S] and a [2Fe-2S] cluster. In every reaction cycle, the enzyme consumes two molecules of AdoMet, each producing 5'-deoxyadenosine (dAH) and a putative dethiobiotinyl carbon radical. The first half reaction results in the hydrogen abstraction from C6 in dithiobiotin (DTB) and initial sulfur addition. Reaction with another equivalent of AdoMet results in abstraction of the C6 methylene pro-S hydrogen atom from 9-mercaptodethiobiotin (MTDB), and the resulting carbon radical is quenched via formation of an intramolecular C-S bond, thus closing the biotin thiophane ring. The sulfur donor [S] is believed to be the [2Fe-2S] cluster, which is sacrificed in the process, so that in vitro the reaction is a single turnover. In vivo, the [2Fe-2S] cluster can be reassembled by the Isc or Suf iron-sulfur cluster assembly systems, to allow further catalysis.
It has been demonstrated that biotin formation proceeds in a stepwise manner, with only one monomer within the dimeric enzyme undergoing turnover to form biotin. The second monomer binds substrates, but does not undergo a reaction, i.e. the enzyme is half-site active. Further, the dAH and methionine generated during the first half-reaction (conversion of DTB to MDTB) can competitively compete with AdoMet during the second half-reaction, preventing the conversion of MDTB to biotin.
Vey JL, Drennan CL.
Structural insights into radical generation by the radical SAM superfamily
▸ Abstract
Chem Rev. 2011;111(4):2487-2506 | PubMed ID: 21370834
Taylor AM, Stoll S, Britt RD, Jarrett JT.
Reduction of the [2Fe-2S] cluster accompanies formation of the intermediate 9-mercaptodethiobiotin in Escherichia coli biotin synthase
▸ Abstract
Biochemistry 2011;50(37):7953-7963 | PubMed ID: 21859080
Phalip V, Lemoine Y, Jeltsch JM.
Cloning of Schizosaccharomyces pombe bio2 by heterologous complementation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant
▸ Abstract
Curr Microbiol. 1999;39(6):348-350 | PubMed ID: 10525840
Lotierzo M, Tse Sum Bui B, Florentin D, Escalettes F, Marquet A.
Biotin synthase mechanism: an overview
▸ Abstract
Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33(4):820-823 | PubMed ID: 16042606
No notes.
Static File Downloads
| File Name | Description | Parameters | Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| repnet.fam272.th50.pE20.mek250K.xgmml | Representative network: each node is a group of similar sequences | node similarity threshold = 50 max edge count = 250K min -log10 E = 20 |
size = 2.4M num_edges = 630 num_nodes = 36 |
| sfld_alignment_fam272.msa | Annotated Sequence Alignment, Stockholm format | 327 sequences size: 166K |
Active Site
Catalyzed Reaction(s)
 |
+ 2 | 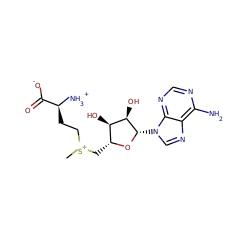 |
+ |  |
+ 2 | 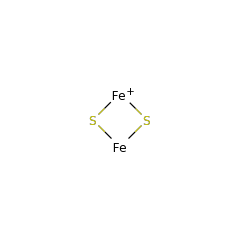 |
 |
 |
+ 2 | 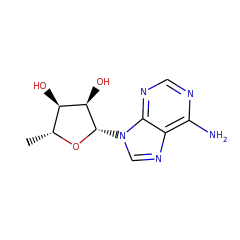 |
+ 2 | 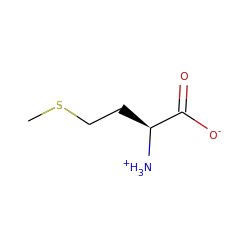 |
+ | 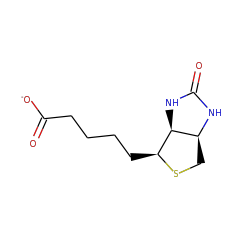 |
+ 2 |  |
||
| thiol group 29917 |
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion 59789 |
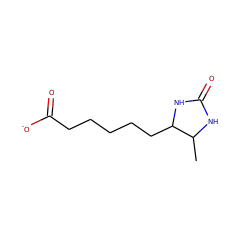
dethiobiotin(1-) 57861 |
di-mu-sulfido-diiron(1+) 33738 |
H group 64428 |
5'-deoxyadenosine 17319 |
L-methionine zwitterion 57844 |
biotinate 57586 |
di-mu-sulfido-diiron(2+) 33737 |
EC: | IntEnz: | Kegg: | BioCyc: | BRENDA: |