Top Level Name
⌊ Superfamily (core) Radical SAM
⌊ Subgroup SPASM/twitch domain containing
| Total |
100%  |
<100%  |
|||
| Functional domains | 1061 | 1034 | 27 | ||
| UniProtKB | 2408 | 2385 | 23 | ||
| GI | 4601 | 4552 | 49 | ||
| Structures | 0 | ||||
| Reactions | 1 | ||||
| Functional domains of this family were last updated on June 10, 2017 | |||||
| New functional domains were last added to this family on June 22, 2014 | |||||
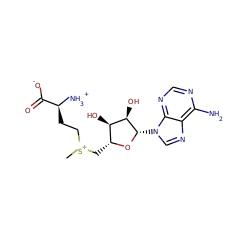
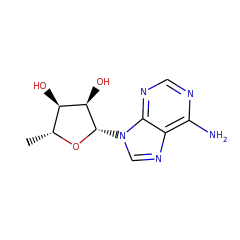
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (4,5-dihydro-4,5-dioxo-1H-pyrrolo-[2,3-f]quinoline-2,7,9-tricarboxylic acid: PQQ) is a water soluble, heat-stable, tricyclic ortho-quinone. It serves as redox cofactor for various bacterial dehydrogenases. It is synthesised from two residues (Glu and Tyr) encoded in the precursor peptide PqqA. Several genes (PqqA-G) are required to derive PQQ from these Glu and Tyr. A likely candidate for catalysing the first step in PQQ formation, the linkage between the C98 of Glu and C9a of Tyr, is PqqE. This is because it is the only enzyme in the pathway with significant sequence similarity to other radical SAM proteins capable of catalysing C-C bond formation. The reaction catalyzed by PqqE is a radical driven C-C bond formation required to link the glutamate and tyrosine moieties at atoms C9 and C9a of PQQ. The exact mechanism is unknown but the analogy to radical SAM proteins implies the following mechanism: The reduced 4Fe-4S cluster transfers an electron to the sulfur of SAM. The C5'-S+ bond of SAM is cleaved, producing methionine and a highly oxidizing 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical. The radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from the tyrosine in PqqA, creating a tyrosine radical at position C9a. The radical reacts with atom C9 of glutamate leading to cyclisation. The exact role of SAM is not yet known.
Puehringer S, Metlitzky M, Schwarzenbacher R
The pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis pathway revisited: a structural approach
▸ Abstract
BMC Biochem. 2008;9(8):None-None | PubMed ID: 18371220
Saichana N, Tanizawa K, Pechoušek J, Novák P, Yakushi T, Toyama H, Frébortová J
PqqE from Methylobacterium extorquens AM1: a radical S-adenosyl-l-methionine enzyme with an unusual tolerance to oxygen
▸ Abstract
J Biochem 2015;None(None):None-None | PubMed ID: 26188050
Barr I, Latham JA, Iavarone AT, Chantarojsiri T, Hwang JD, Klinman JP
Demonstration That the Radical S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) Enzyme PqqE Catalyzes de Novo Carbon-Carbon Cross-linking within a Peptide Substrate PqqA in the Presence of the Peptide Chaperone PqqD
▸ Abstract
J Biol Chem 2016;291(17):8877-8884 | PubMed ID: 26961875
PqqE is a 380 residue protein with a molecular mass of 43 kDA and a theoretical pI of about 5.7. An FFAS search revealed significant homologies with proteins from the radical SAM protein family. The best homologue was Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis protein A (PDB ID: 1tv7) which was, therefore, used as a template for homology modelling. Because the homologue has such a good score (6.7 times lower than the threshold of -9.5) we have a reliable model for amino acids 5 to 333 in PqqE. It is concluded that PqqE is a family member of radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) enzymes, because its sequence suggests that it contains a SAM domain with an iron-sulfur cluster. The four iron atoms of the cluster are coordinated by three cysteines (C26, C30, C33) from the conserved CxxxCxxC (C, Cys; x, any amino acid) motif of radical SAM enzymes and one atom is coordinated by the SAM (Figure ?(Figure9C)9C) PqqE-related enzymes often contain a Y at residue 27(Tyr) and have therefore a CxxxCxYC pattern.
Static File Downloads
| File Name | Description | Parameters | Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| network.fam280.bs60.mek250K.xgmml | One node per sequence network | min bit score = 60 max edge count = 250K |
size = 130M num_edges = 250000 num_nodes = 1061 |
| sfld_alignment_fam280.msa | Annotated Sequence Alignment, Stockholm format | 318 sequences size: 147K |