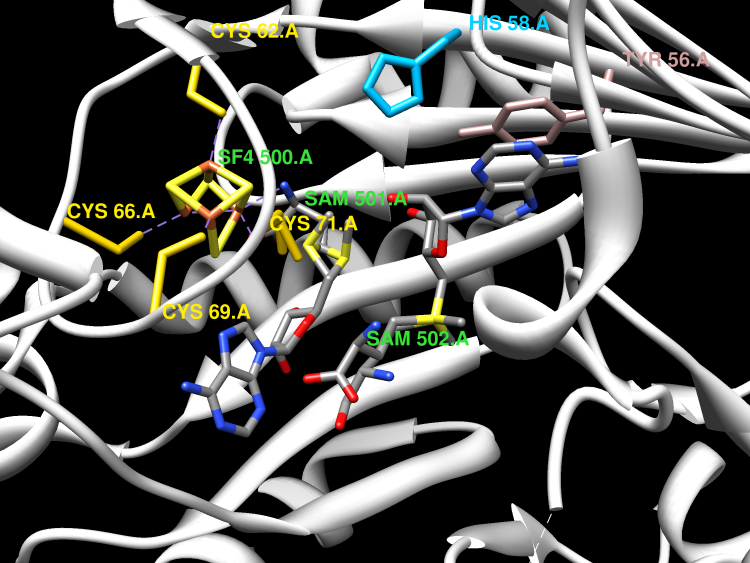
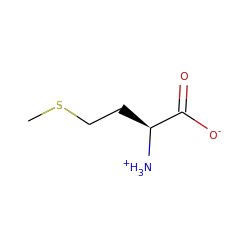
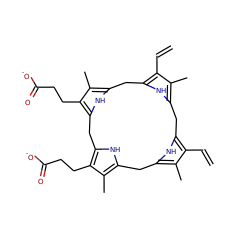
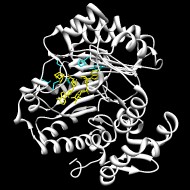
Biosynthesis of heme and chlorophyll requires coproporphyrinogen III to be converted to protoporphyrinogen IX by oxidatively decarboxylating the propionate side chains of rings A and B to the corresponding vinyl group. The oxygen independent protein, HemN, catalyses this essential conversion. HemN is a monomeric protein consisting of two distinct domains. The N-terminal domain, significantly larger than the C-terminal domain, comprises residues 36±364. The function of the C-terminal domain is still unknown.
Layer G, Moser J, Heinz DW, Jahn D, Schubert WD
Crystal structure of coproporphyrinogen III oxidase reveals cofactor geometry of Radical SAM enzymes
▸ Abstract
'Radical SAM' enzymes generate catalytic radicals by combining a 4Fe-4S cluster and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in close proximity. We present the first crystal structure of a Radical SAM enzyme, that of HemN, the Escherichia coli oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen III oxidase, at 2.07 A resolution. HemN catalyzes the essential conversion of coproporphyrinogen III to protoporphyrinogen IX during heme biosynthesis. HemN binds a 4Fe-4S cluster through three cysteine residues conserved in all Radical SAM enzymes. A juxtaposed SAM coordinates the fourth Fe ion through its amide nitrogen and carboxylate oxygen. The SAM sulfonium sulfur is near both the Fe (3.5 A) and a neighboring sulfur of the cluster (3.6 A), allowing single electron transfer from the 4Fe-4S cluster to the SAM sulfonium. SAM is cleaved yielding a highly oxidizing 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical. HemN, strikingly, binds a second SAM immediately adjacent to the first. It may thus successively catalyze two propionate decarboxylations. The structure of HemN reveals the cofactor geometry required for Radical SAM catalysis and sets the stage for the development of inhibitors with antibacterial function due to the uniquely bacterial occurrence of the enzyme.
EMBO J
2003;22(23):6214-6224
| PubMed ID:
14633981
Layer G, Grage K, Teschner T, Schünemann V, Breckau D, Masoumi A, Jahn M, Heathcote P, Trautwein AX, Jahn D
Radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme coproporphyrinogen III oxidase HemN: functional features of the [4Fe-4S] cluster and the two bound S-adenosyl-L-methionines
▸ Abstract
The S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) radical enzyme oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen III oxidase HemN catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of coproporphyrinogen III to protoporphyrinogen IX during bacterial heme biosynthesis. The recently solved crystal structure of Escherichia coli HemN revealed the presence of an unusually coordinated iron-sulfur cluster and two molecules of AdoMet. EPR spectroscopy of the reduced iron-sulfur center in anaerobically purified HemN in the absence of AdoMet has revealed a [4Fe-4S](1+) cluster in two slightly different conformations. Mössbauer spectroscopy of anaerobically purified HemN has identified a predominantly [4Fe-4S](2+) cluster in which only three iron atoms were coordinated by cysteine residues (isomer shift of delta = 0.43 (1) mm/s). The fourth non-cysteine-ligated iron exhibited a delta = 0.57 (3) mm/s, which shifted to a delta = 0.68 (3) mm/s upon addition of AdoMet. Substrate binding by HemN did not alter AdoMet coordination to the cluster. Multiple rounds of AdoMet cleavage with the formation of the reaction product methionine indicated AdoMet consumption during catalysis and identified AdoMet as a co-substrate for HemN catalysis. AdoMet cleavage was found to be dependent on the presence of the substrate coproporphyrinogen III. Two molecules of AdoMet were cleaved during one catalytic cycle for the formation of one molecule of protoporphyrinogen IX. Finally, the binding site for the unusual second, non iron-sulfur cluster coordinating AdoMet molecule (AdoMet2) was targeted using site-directed mutagenesis. All AdoMet2 binding site mutants still contained an iron-sulfur cluster and most still exhibited AdoMet cleavage, albeit reduced compared with the wild-type enzyme. However, all mutants lost their overall catalytic ability indicating a functional role for AdoMet2 in HemN catalysis. The reported significant correlation of structural and functional biophysical and biochemical data identifies HemN as a useful model system for the elucidation of general AdoMet radical enzyme features.
J Biol Chem.
2005;280(32):29038-29046
| PubMed ID:
15967800
Layer G, Verfürth K, Mahlitz E, Jahn D
Oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase HemN from Escherichia coli
▸ Abstract
In bacteria the oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase catalyzes the oxygen-independent conversion of coproporphyrinogen-III to protoporphyrinogen-IX. The Escherichia coli hemN gene encoding a putative part of this enzyme was overexpressed in E. coli. Anaerobically purified HemN is a monomeric protein with a native M(r) = 52,000 +/- 5,000. A newly established anaerobic enzyme assay was used to demonstrate for the first time in vitro coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase activity for recombinant purified HemN. The enzyme requires S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM), NAD(P)H, and additional cytoplasmatic components for catalysis. An oxygen-sensitive iron-sulfur cluster was identified by absorption spectroscopy and iron analysis. Cysteine residues Cys(62), Cys(66), and Cys(69), which are part of the conserved CXXXCXXC motif found in all HemN proteins, are essential for iron-sulfur cluster formation and enzyme function. Completely conserved residues Tyr(56) and His(58), localized closely to the cysteine-rich motif, were found to be important for iron-sulfur cluster integrity. Mutation of Gly(111) and Gly(113), which are part of the potential GGGTP S-adenosyl-l-methionine binding motif, completely abolished enzymatic function. Observed functional properties in combination with a recently published computer-based enzyme classification (Sofia, H. J., Chen, G., Hetzler, B. G., Reyes-Spindola, J. F., and Miller, N. E. (2001) Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 1097-1106) identifies HemN as "Radical SAM enzyme." An appropriate enzymatic mechanism is suggested.
J Biol Chem.
2002;277(37):34136-34142
| PubMed ID:
12114526
Dailey HA, Gerdes S, Dailey TA, Burch JS, Phillips JD
Noncanonical coproporphyrin-dependent bacterial heme biosynthesis pathway that does not use protoporphyrin
▸ Abstract
It has been generally accepted that biosynthesis of protoheme (heme) uses a common set of core metabolic intermediates that includes protoporphyrin. Herein, we show that the Actinobacteria and Firmicutes (high-GC and low-GC Gram-positive bacteria) are unable to synthesize protoporphyrin. Instead, they oxidize coproporphyrinogen to coproporphyrin, insert ferrous iron to make Fe-coproporphyrin (coproheme), and then decarboxylate coproheme to generate protoheme. This pathway is specified by three genes named hemY, hemH, and hemQ. The analysis of 982 representative prokaryotic genomes is consistent with this pathway being the most ancient heme synthesis pathway in the Eubacteria. Our results identifying a previously unknown branch of tetrapyrrole synthesis support a significant shift from current models for the evolution of bacterial heme and chlorophyll synthesis. Because some organisms that possess this coproporphyrin-dependent branch are major causes of human disease, HemQ is a novel pharmacological target of significant therapeutic relevance, particularly given high rates of antimicrobial resistance among these pathogens.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
2015;112(7):2210-2215
| PubMed ID:
25646457
In order to perform this function, proteins in this family must have a GPRYTSYPTA and RNFQGYTT motif in the sequence.
Remains as a single cluster up to E() -93.