Zhang Q, van der Donk WA, Liu W
Radical-mediated enzymatic methylation: a tale of two SAMS
▸ Abstract
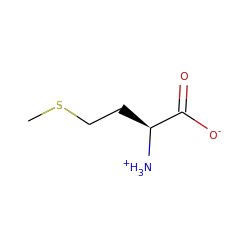
Methylation is an essential and ubiquitous reaction that plays an important role in a wide range of biological processes. Most biological methylations use S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl donor and proceed via an S(N)2 displacement mechanism. However, researchers have discovered an increasing number of methylations that involve radical chemistry. The enzymes known to catalyze these reactions all belong to the radical SAM superfamily. This family of enzymes utilizes a specialized [4Fe-4S] cluster for reductive cleavage of SAM to yield a highly reactive 5'-deoxyadenosyl (dAdo) radical. Radical chemistry is then imposed on a variety of organic substrates, leading to a diverse array of transformations. Until recently, researchers had not fully understood how these enzymes employ radical chemistry to mediate a methyl transfer reaction. Sequence analyses reveal that the currently identified radical SAM methyltransferases (RSMTs) can be grouped into three classes, which appear distinct in protein architecture and mechanism. Class A RSMTs mainly include the rRNA methyltransferases RlmN and Cfr from various origins. As exemplified by Escherichia coli RlmN, these proteins have a single canonical radical SAM core domain that includes an (βα)(6) partial barrel most similar to that of pyruvate formate lyase-activase. The exciting recent studies on RlmN and Cfr are beginning to provide insights into the intriguing chemistry of class A RSMTs. These enzymes utilize a methylene radical generated on a unique methylated cysteine residue. However, based on the variety of substrates used by the other classes of RSMTs, alternative mechanisms are likely to be discovered. Class B RSMTs contain a proposed N-terminal cobalamin binding domain in addition to a radical SAM domain at the C-terminus. This class of proteins methylates diverse substrates at inert sp(3) carbons, aromatic heterocycles, and phosphinates, possibly involving a cobalamin-mediated methyl transfer process. Class C RSMTs share significant sequence similarity with coproporphyrinogen III oxidase HemN. Despite methylating similar substrates (aromatic heterocycles), class C RSMTs likely employ a mechanism distinct from that of class A because two conserved cysteines that are required for class A are typically not found in class C RSMTs. Class A and class B enzymes probably share the use of two molecules of SAM: one to generate a dAdo radical and one to provide the methyl group to the substrate. In class A, a cysteine would act as a conduit of the methyl group whereas in class B cobalamin may serve this purpose. Currently no clues are available regarding the mechanism of class C RSMTs, but the sequence similarities between its members and HemN and the observation that HemN binds two SAM molecules suggest that class C enzymes could use two SAM molecules for catalysis. The diverse strategies for using two SAM molecules reflect the rich chemistry of radical-mediated methylation reactions and the remarkable versatility of the radical SAM superfamily.
Acc Chem Res
2012;45(4):555-564
| PubMed ID:
22097883
Yan F, Fujimori DG
RNA methylation by radical SAM enzymes RlmN and Cfr proceeds via methylene transfer and hydride shift
▸ Abstract
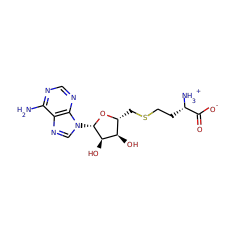
RlmN and Cfr are Radical SAM enzymes that modify a single adenosine nucleotide--A2503--in 23S ribosomal RNA. This nucleotide is positioned within the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome, which is a target of numerous antibiotics. An unusual feature of these enzymes is their ability to carry out methylation of amidine carbons of the adenosine substrate. To gain insight into the mechanism of methylation catalyzed by RlmN and Cfr, deuterium labeling experiments were carried out. These experiments demonstrate that the newly introduced methyl group is assembled from an S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-derived methylene fragment and a hydrogen atom that had migrated from the substrate amidine carbon. Rather than activating the adenosine nucleotide of the substrate by hydrogen atom abstraction from an amidine carbon, the 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical abstracts hydrogen from the second equivalent of SAM to form the SAM-derived radical cation. This species, or its corresponding sulfur ylide, subsequently adds into the substrate, initiating hydride shift and S-adenosylhomocysteine elimination to complete the formation of the methyl group. These findings indicate that rather than acting as methyltransferases, RlmN and Cfr are methyl synthases. Together with the previously described 5'-deoxyadenosyl and 3-amino-3-carboxypropyl radicals, these findings demonstrate that all three carbon atoms attached to the sulfonium center in SAM can serve as precursors to carbon-derived radicals in enzymatic reactions.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
2011;108(10):3930-3934
| PubMed ID:
21368151
Yan F, LaMarre JM, Röhrich R, Wiesner J, Jomaa H, Mankin AS, Fujimori DG
RlmN and Cfr are radical SAM enzymes involved in methylation of ribosomal RNA
▸ Abstract
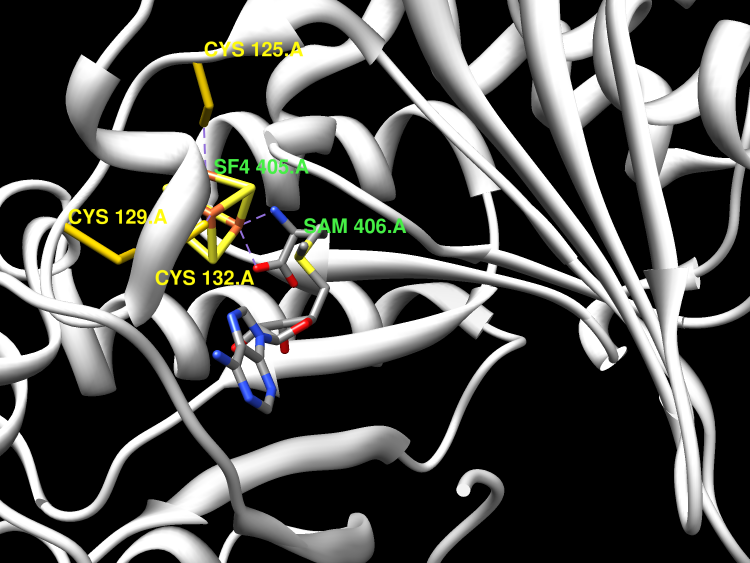
Posttranscriptional modifications of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) nucleotides are a common mechanism of modulating the ribosome's function and conferring bacterial resistance to ribosome-targeting antibiotics. One such modification is methylation of an adenosine nucleotide within the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome mediated by the endogenous methyltransferase RlmN and its evolutionarily related resistance enzyme Cfr. These methyltransferases catalyze methyl transfer to aromatic carbon atoms of the adenosine within a complex 23S rRNA substrate to form the 2,8-dimethylated product. RlmN and Cfr are members of the Radical SAM superfamily and contain the characteristic cysteine-rich CX(3)CX(2)C motif. We demonstrate that both enzymes are capable of accommodating the requisite [4Fe-4S] cluster. S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) is both the methyl donor and the source of a 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical, which activates the substrate for methylation. Detailed analyses of the rRNA requirements show that the enzymes can utilize protein-free 23S rRNA as a substrate, but not the fully assembled large ribosomal subunit, suggesting that the methylations take place during the assembly of the ribosome. The key recognition elements in the 23S rRNA are helices 90-92 and the adjacent single stranded RNA that encompasses A2503. To our knowledge, this study represents the first in vitro description of a methyl transfer catalyzed by a member of the Radical SAM superfamily, and it expands the catalytic repertoire of this diverse enzyme class. Furthermore, by providing information on both the timing of methylation and its substrate requirements, our findings have important implications for the functional consequences of Cfr-mediated modification of rRNA in the acquisition of antibiotic resistance.
J Am Chem Soc
2010;132(11):3953-3964
| PubMed ID:
20184321
Fujimori DG
Radical SAM-mediated methylation reactions
▸ Abstract
A subset of enzymes that belong to the radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) superfamily is able to catalyze methylation reactions. Substrates of these enzymes are distinct from the nucleophilic substrates that undergo methylation by a polar mechanism. Recently, activities of several radical SAM methylating enzymes have been reconstituted in vitro and their mechanisms of catalysis investigated. The RNA modifying enzymes RlmN and Cfr catalyze methylation via a methyl synthase mechanism. These enzymes use SAM in two distinct roles: as a source of a methyl group transferred to a conserved cysteine and as a source of 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical (5'-dA). Hydrogen atom abstraction by this species generates a thiomethylene radical which adds into the RNA substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate covalent adduct. In another recent study, methylation of the indole moiety of tryptophan by the radical SAM and cobalamin-binding domain enzyme TsrM has been reconstituted. Methylcobalamin serves as an intermediate methyl donor in TsrM, and is proposed to transfer the methyl group as a methyl radical. Interestingly, despite the presence of the radical SAM motif, no reductive cleavage of SAM has been observed in this methylation. These important reconstitutions set the stage for further studies on mechanisms of radical methylation.
Curr Opin Chem Biol
2013;17(4):597-604
| PubMed ID:
23835516
Schwalm EL, Grove TL, Booker SJ, Boal AK
Crystallographic capture of a radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme in the act of modifying tRNA
▸ Abstract
RlmN is a dual-specificity RNA methylase that modifies C2 of adenosine 2503 (A2503) in 23S rRNA and C2 of adenosine 37 (A37) in several Escherichia coli transfer RNAs (tRNAs). A related methylase, Cfr, modifies C8 of A2503 via a similar mechanism, conferring resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics. Here, we report the x-ray structure of a key intermediate in the RlmN reaction, in which a Cys(118)→Ala variant of the protein is cross-linked to a tRNA(Glu)substrate through the terminal methylene carbon of a formerly methylcysteinyl residue and C2 of A37. RlmN contacts the entire length of tRNA(Glu), accessing A37 by using an induced-fit strategy that completely unfolds the tRNA anticodon stem-loop, which is likely critical for recognition of both tRNA and ribosomal RNA substrates.
Science
2016;352(6283):309-312
| PubMed ID:
27081063